Importance reweighting example
"""
Script to test importance reweighting
In this script we generate data according to
y = m x + c + Normal(0, sigma)
Then
1) Calculate the "full" posterior P(m, c | data)
2) Calculate the "partial" posterior P(m | data, c=0) (note c=0 in the injection)
3) Use importance reweighting to calculate P(m| data) from the "partial" results
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import bilby
from scipy.special import logsumexp
import tqdm
np.random.seed(1234)
outdir = '.'
sampler = 'dynesty'
npoints = 5000
def marginalized_log_likelihood_over_c(m, likelihood):
""" Calculates L(data| m), marginalized over c
Parameters
----------
m: float
The fixed value of m at which to calculate the marginalized likelihood
likelihood: bilby.core.likelihood.Likelihood instance
Used to evaluate the log likelihood
Note
----
Integration range chosen to cover the region of interest. Note, this
neglects the normalization factors which don't count in the weight
calculation.
"""
likelihood.parameters['m'] = m
c_array = np.linspace(-0.2, 0.2, 100)
integrand = []
for c in c_array:
likelihood.parameters['c'] = c
integrand.append(likelihood.log_likelihood())
return logsumexp(integrand)
def model(x, m, c):
return m * x + c
# Injection parameters and create data
m = 1
c = 0
sigma = 0.1
N = 100
x = np.linspace(0, 1, N)
y = model(x, m, c) + np.random.normal(0, sigma, N)
likelihood = bilby.core.likelihood.GaussianLikelihood(x, y, model)
# Run the full PE
priors = dict()
priors['m'] = bilby.core.prior.Uniform(0, 5, 'm')
priors['c'] = bilby.core.prior.Uniform(-2, 2, 'c')
priors['sigma'] = sigma
full_result = bilby.run_sampler(
likelihood=likelihood, priors=priors, sampler=sampler, npoints=npoints,
outdir=outdir, label='full')
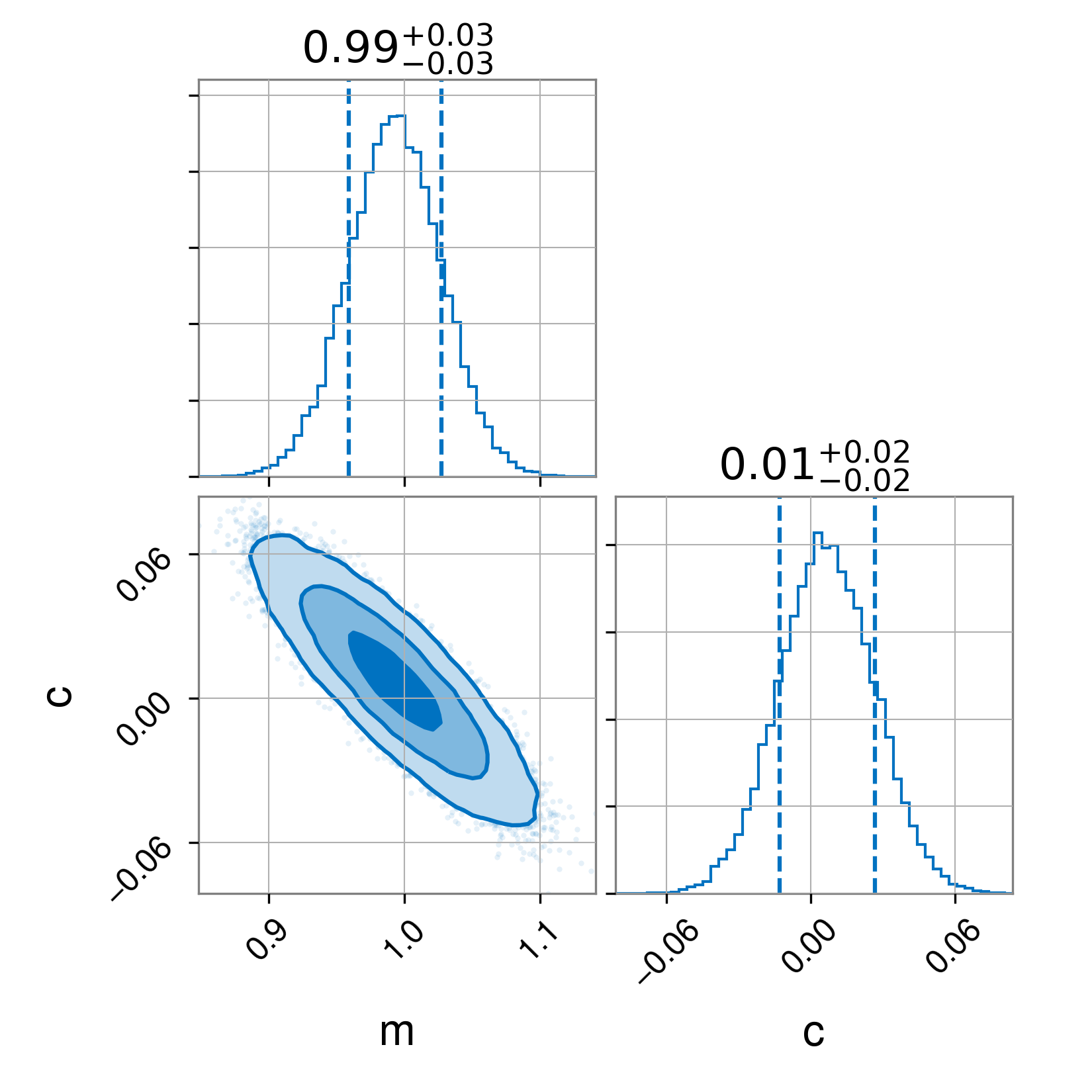
full_result.plot_corner()
# Run the constrained PE
priors = dict()
priors['m'] = bilby.core.prior.Uniform(0, 5, 'm')
priors['c'] = 0
priors['sigma'] = sigma
partial_result = bilby.run_sampler(
likelihood=likelihood, priors=priors, sampler=sampler, npoints=npoints,
outdir=outdir, label='partial')
partial_result.plot_corner()
# Pull out the uniformly-weighted samples from the full and partial runs
full_m_samples = full_result.posterior.m.values
partial_m_samples = partial_result.posterior.m.values
# Calculate primed likelihood
log_likelihood_prime = []
for m in tqdm.tqdm(partial_m_samples):
log_likelihood_prime.append(marginalized_log_likelihood_over_c(m, likelihood))
log_likelihood_prime = np.array(log_likelihood_prime)
# Calculate p, the normalized probably for each sample in partial_m_samples
log_likelihood = partial_result.posterior.log_likelihood.values
weights = log_likelihood_prime - log_likelihood
p = np.exp(weights)
p /= np.sum(p)
# Reweight to get corrected samples
reweight_samples = np.random.choice(partial_m_samples, size=30000, p=p)
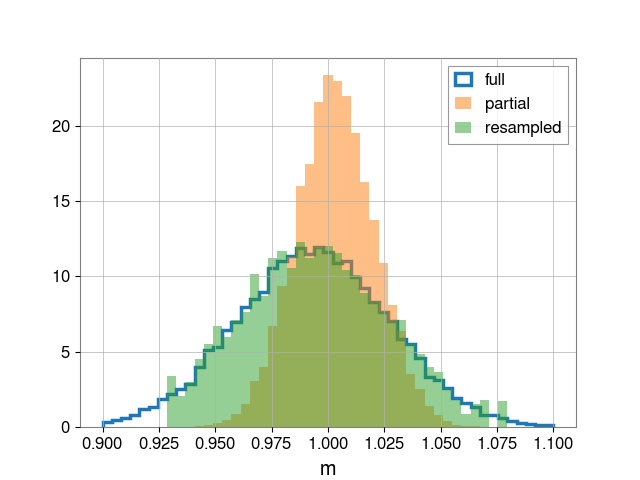
# Plot
bins = np.linspace(0.9, 1.1, 50)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.hist(full_m_samples, bins=bins, density=True, label="full",
histtype='step', linewidth=2.5)
ax.hist(partial_m_samples, bins=bins, density=True, alpha=0.5, label="partial")
ax.hist(reweight_samples, bins=bins, density=True, alpha=0.5, label="resampled")
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel("m")
plt.savefig("posterior")
Having run this script, we obtain three images. First, the full posterior
Second, the posterior when fixing c=0
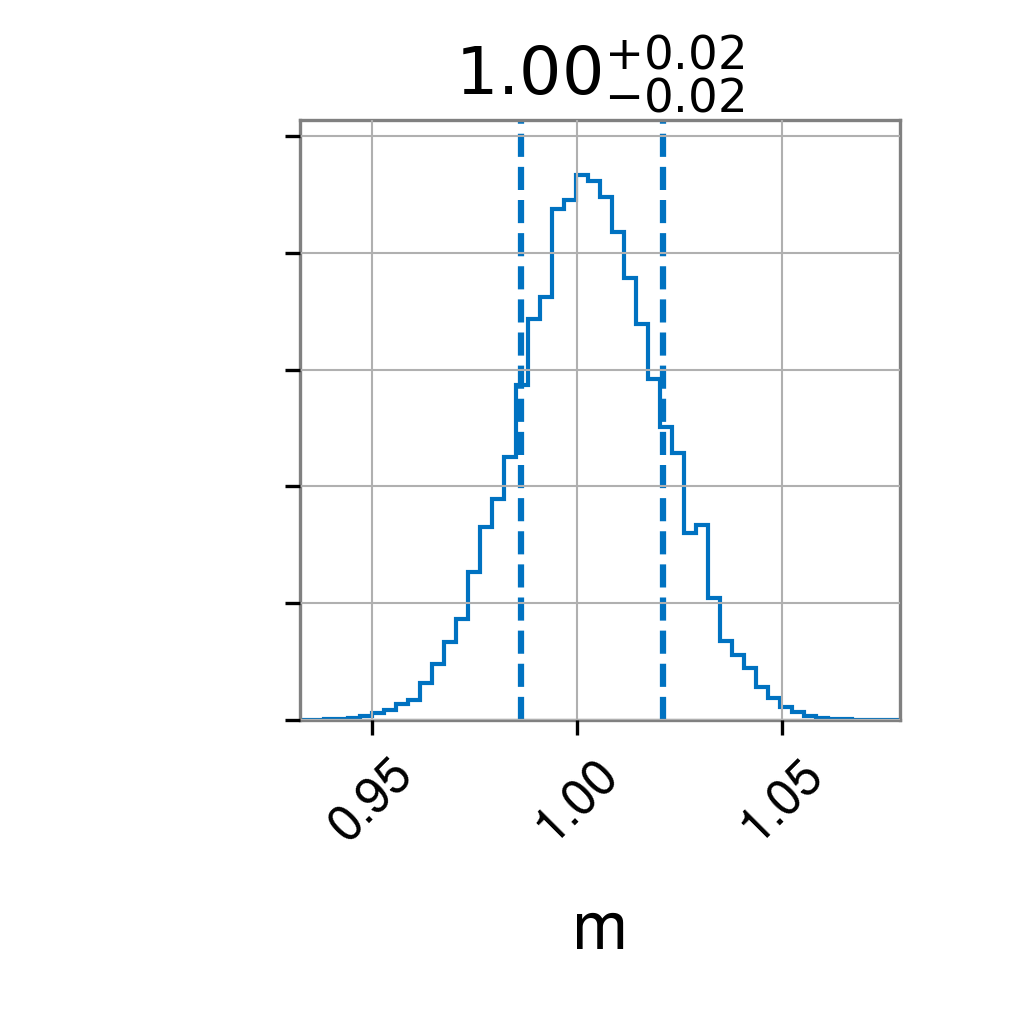
Finally, the rewighted posterior from fixed case